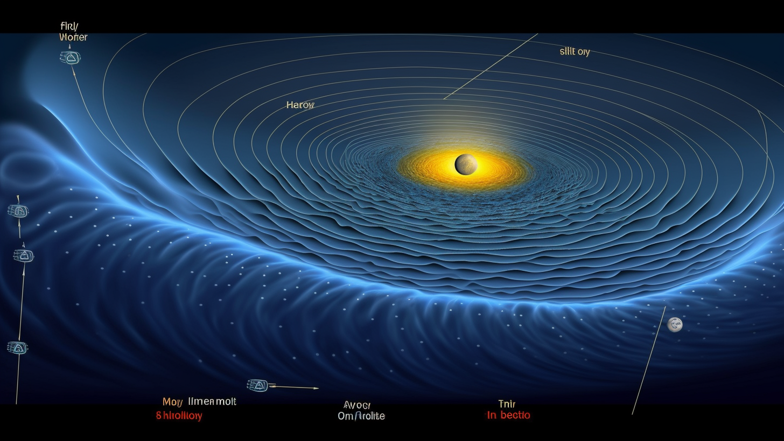
Gravitational waves are ripples in the fabric of space-time. They are produced by the acceleration of massive objects such as black holes, neutron stars, and supernovae. According to Einstein's theory of relativity, these waves are created when two massive objects orbit each other, emitting waves of energy that propagate outward at the speed of light.
The first detection of gravitational waves was made in 2015 by the LIGO (Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory) collaboration, a group of scientists from around the world. This discovery was hailed as one of the most important scientific breakthroughs of the century and a milestone in the history of astrophysics.
Since then, there have been numerous detections of gravitational waves, each providing new insights into the workings of our universe. These observations have not only confirmed Einstein's theory of relativity but have also shed light on some of the most perplexing questions in astrophysics.
One of the biggest accomplishments of gravitational wave astronomy is the detection of black hole mergers. Black holes are some of the most mysterious objects in the universe, and their mergers create some of the most powerful and violent events known to humankind. When two black holes merge, they release a tremendous amount of energy in the form of gravitational waves that can be detected by instruments on Earth.
The detection of these waves has helped us understand the properties of black holes and their behavior. It has also given scientists a new way of studying the universe and its contents, opening up new possibilities for exploration and discovery.
Gravitational wave astronomy has also provided us with new insights into the origins of the universe itself. The Big Bang theory is the most widely accepted scientific explanation for the creation of the universe. However, there are still some questions that remain unanswered, such as what happened in the first few moments after the Big Bang.
Gravitational waves allow us to look back in time, providing a window into the first seconds of the universe's existence. By detecting these waves, scientists can study the universe's earliest moments and gain a better understanding of its evolution since then.
In addition to black holes, gravitational waves can also be produced by neutron stars, which are the densest objects in the universe. When two neutron stars merge, they create an explosion called a kilonova, which releases a vast amount of energy in the form of electromagnetic radiation and gravitational waves.
The detection of kilonovae has allowed us to study neutron stars and their properties in more detail. It has also provided us with new insights into the composition of the universe and the elements that make up the stars and planets.
Another exciting application of gravitational wave astronomy is the possibility of detecting gravitational waves from the early universe, which could give us insight into the origins of the universe itself. This is an area of ongoing research, and scientists are working to develop new technologies and techniques to make this possible.
In conclusion, gravitational waves are a fascinating and exciting area of study in astrophysics. They have revolutionized our understanding of the universe and are leading to new discoveries that are changing the way we view the cosmos.
The Ripple Effect of gravitational waves has already brought us many exciting discoveries, from black hole mergers to the origins of the universe. There is no doubt that this field will continue to provide us with new insights and a deeper understanding of our universe and its mysteries for many years to come.
Comments
Post a Comment